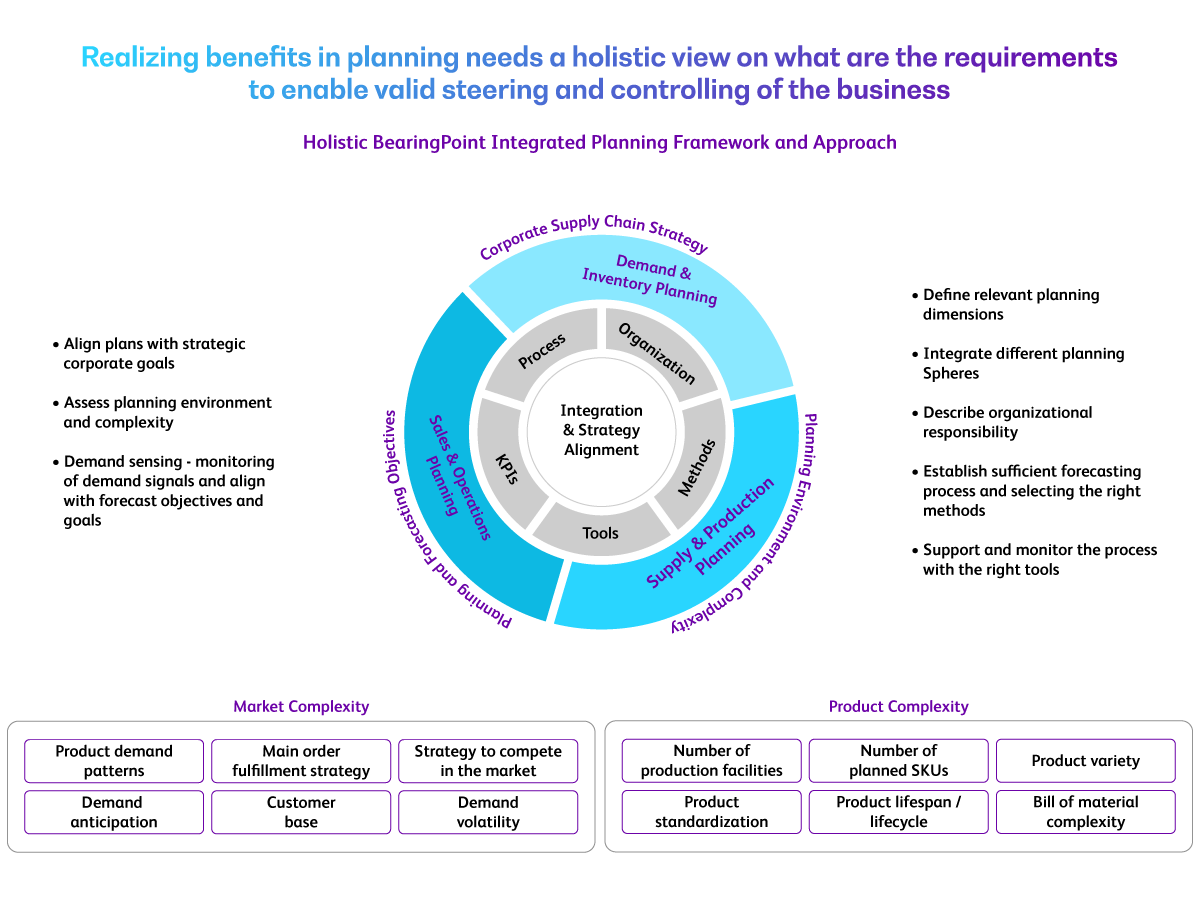
Machinists work with a variety of machines. These machines are used to repair products made of metal, such as cars. These machines can also produce precision metal parts and create new alloys. Machinists can be exposed to toxic substances. A good machinist is detail-oriented, has strong communication skills, and is able to interpret mechanical blueprints.
Part-time and full-time work are common for machinists. Many begin their career right out of highschool. Some machinists take an apprenticeship before they move on to a fulltime position. Others may pursue associate degrees. Some machinists can even pursue an engineering degree or computer-aided design degree (CAD).
Many machinists work in factories or special shops. Although these positions are noisy and can expose you to potentially dangerous materials, they offer great opportunities for problem solving. Machinists use manual and automatic machines. For those with more experience, it is possible to rise up to managerial and supervisory roles. With the retirement of baby boomers, the need for machinists grows. As machine shops modernize for automation, job security increases.
Depending upon the employer, machinists are often assigned specific duties. These include setting up machines and maintaining them. They can also work on assembly lines, which are machines that are operated by a human or a robot. Other responsibilities include programming the machines and monitoring them, and reading blueprints.
Machinists have to work with many different materials like steel, aluminum (brass), copper, and other metals. While most machinists work with machines that make metal parts, it is not uncommon for them to be required to work with other materials.
Machine operators generally have a highschool diploma. Some employers may require an associate’s degree. You can begin a four-year program if you're interested in becoming a Machinist. For more experience and knowledge, you may also be able to work with a mentor within your company. Ask your mentor about additional training opportunities, such as apprenticeships and higher education.
Machinists need to work together, regardless of company. You can work with them in a group or alone. However, they must follow safety procedures. This includes wearing proper safety equipment, such as earplugs, gloves, and masks. Machinists may also be exposed to chemicals, fumes, or other environmental hazards. Machinists aren't always under constant pressure.

Besides on-the-job training, machinists can enroll in college courses or join trade unions. Machine operators who join unions enjoy greater job security and better benefits. The majority of union members are eligible for health insurance or retirement plans. A number of colleges offer two-year machining associates degrees.
With a degree in machinist work, you can move up the corporate ladder. As the demand for car parts increases, machinists will be needed more and more. The projected growth in job opportunities between 2020-2030 is 7%. Machine operators will be in high demand for the next 20 years, thanks to increasing use of artificial intelligence, and retooling for automated manufacturing.
FAQ
Why automate your warehouse
Modern warehousing is becoming more automated. Increased demand for efficient and faster delivery has resulted in a rise in e-commerce.
Warehouses should be able adapt quickly to new needs. To do so, they must invest heavily in technology. Automation of warehouses offers many benefits. Here are some benefits of investing in automation
-
Increases throughput/productivity
-
Reduces errors
-
Increases accuracy
-
Safety is boosted
-
Eliminates bottlenecks
-
Companies can scale more easily
-
It makes workers more efficient
-
The warehouse can be viewed from all angles.
-
Enhances customer experience
-
Improves employee satisfaction
-
This reduces downtime while increasing uptime
-
This ensures that quality products are delivered promptly
-
Removes human error
-
This helps to ensure compliance with regulations
Can we automate some parts of manufacturing?
Yes! Yes. Automation has been around since ancient time. The Egyptians invent the wheel thousands of year ago. Nowadays, we use robots for assembly lines.
There are many uses of robotics today in manufacturing. They include:
-
Assembly line robots
-
Robot welding
-
Robot painting
-
Robotics inspection
-
Robots that create products
Manufacturing could also benefit from automation in other ways. 3D printing is a way to make custom products quickly and without waiting weeks or months for them to be manufactured.
What are the four types in manufacturing?
Manufacturing refers the process of turning raw materials into useful products with machines and processes. It includes many different activities like designing, building and testing, packaging, shipping and selling, as well as servicing.
What is the importance of logistics in manufacturing?
Logistics are essential to any business. They help you achieve great results by helping you manage all aspects of product flow, from raw materials to finished goods.
Logistics also play a major role in reducing costs and increasing efficiency.
Statistics
- Many factories witnessed a 30% increase in output due to the shift to electric motors. (en.wikipedia.org)
- According to a Statista study, U.S. businesses spent $1.63 trillion on logistics in 2019, moving goods from origin to end user through various supply chain network segments. (netsuite.com)
- It's estimated that 10.8% of the U.S. GDP in 2020 was contributed to manufacturing. (investopedia.com)
- [54][55] These are the top 50 countries by the total value of manufacturing output in US dollars for its noted year according to World Bank.[56] (en.wikipedia.org)
- According to the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO), China is the top manufacturer worldwide by 2019 output, producing 28.7% of the total global manufacturing output, followed by the United States, Japan, Germany, and India.[52][53] (en.wikipedia.org)
External Links
How To
How to Use the Just-In-Time Method in Production
Just-in-time is a way to cut costs and increase efficiency in business processes. It's a way to ensure that you get the right resources at just the right time. This means that you only pay for what you actually use. Frederick Taylor developed the concept while working as foreman in early 1900s. After observing how workers were paid overtime for late work, he realized that overtime was a common practice. He realized that workers should have enough time to complete their jobs before they begin work. This would help increase productivity.
JIT is an acronym that means you need to plan ahead so you don’t waste your money. You should also look at the entire project from start to finish and make sure that you have sufficient resources available to deal with any problems that arise during the course of your project. If you anticipate that there might be problems, you'll have enough people and equipment to fix them. This will ensure that you don't spend more money on things that aren't necessary.
There are many types of JIT methods.
-
Demand-driven JIT: You order the parts and materials you need for your project every other day. This will allow to track how much material has been used up. This will allow you to calculate how long it will take to make more.
-
Inventory-based : You can stock the materials you need in advance. This allows for you to anticipate how much you can sell.
-
Project-driven: This method allows you to set aside enough funds for your project. Once you have an idea of how much material you will need, you can purchase the necessary materials.
-
Resource-based JIT : This is probably the most popular type of JIT. You allocate resources based on the demand. You might assign more people to help with orders if there are many. You'll have fewer orders if you have fewer.
-
Cost-based: This is similar to resource-based, except that here you're not just concerned about how many people you have but how much each person costs.
-
Price-based: This is a variant of cost-based. However, instead of focusing on the individual workers' costs, this looks at the total price of the company.
-
Material-based: This approach is similar to cost-based. However, instead of looking at the total cost for the company, you look at how much you spend on average on raw materials.
-
Time-based: Another variation of resource-based JIT. Instead of focusing on the cost of each employee, you will focus on the time it takes to complete a project.
-
Quality-based JIT: Another variation on resource-based JIT. Instead of worrying about the costs of each employee or how long it takes for something to be made, you should think about how quality your product is.
-
Value-based JIT: One of the most recent forms of JIT. In this case, you're not concerned with how well the products perform or whether they meet customer expectations. Instead, your goal is to add value to the market.
-
Stock-based: This inventory-based approach focuses on how many items are being produced at any one time. It is used when production goals are met while inventory is kept to a minimum.
-
Just-in-time planning (JIT): This is a combination JIT and supply-chain management. It is the process that schedules the delivery of components within a short time of their order. It reduces lead times and improves throughput.