
A supply chain management involves many aspects of a company. It covers both internal processes as well as the flow materials and finished products. Marketing also includes supply chain management. Supply chains are used in almost every industry. The main function of the supply chain is to deliver products to consumers. It is our common goal to deliver the products on time.
A manager in operations is responsible for overseeing the business processes. This includes managing the staffing and hiring process. They are responsible for planning and production. They are responsible for developing a strategy to improve operational efficiency. The operations manager is responsible for ensuring that enough inventory is available for production, that it fits within the company budget, and that it conforms to company specifications. To ship orders to customers and retailers, he works in coordination with the supply manager.
The operations and Supply Chain program at UTSA aims for leadership and analytical development. The program is hands-on and combines classroom instruction with experiential learning. The program provides training in data analysis, business improvement, and Lean Six Sigma certification. The program also provides a comprehensive overview of the operations and supply chain industry. The program offers opportunities to explore new technologies as well as to apply these concepts to your own company.
The operations and supply chain program focuses on value-adding processes. This program equips students with the necessary skills to make better business decisions. The program includes a number of case studies and examples from industry. The program also helps students communicate clearly and improve their computer skills. This program also offers minors. The minor is intended to complement the major, and to help students increase the effectiveness of their supply chains. The minor can also be used as a Context and Perspectives course or an unrestricted elective.
Students have the opportunity to learn how to make better business decisions through the operations and supply chain program. It also offers students a unique experience of applying concepts to their own businesses. This can be used as a steppingstone for management, marketing and technology careers. It also allows students to apply for the Lean Six Sigma green belt certification. You can also interact with industry professionals and learn new technologies and trends.
Students will also have the opportunity to learn about the production and distribution of products and services in the operations and supply chains program. It also teaches students the skills of communication, which are essential in business and managerial management.

The book is written in a simple and understandable style. It is suitable for students from a wide range of backgrounds. The book explains the supply chain in detail and also provides case studies that illustrate how to create a supply network. This book also presents quantitative methods of comparing supply and demand. This book also provides information on how to include customers in your supply chain.
FAQ
What are the four types in manufacturing?
Manufacturing is the process of transforming raw materials into useful products using machines and processes. Manufacturing can include many activities such as designing and building, testing, packaging shipping, selling, servicing, and other related activities.
Is it possible to automate certain parts of manufacturing
Yes! Yes! Automation has existed since ancient times. The wheel was invented by the Egyptians thousands of years ago. Robots are now used to assist us in assembly lines.
There are many applications for robotics in manufacturing today. They include:
-
Line robots
-
Robot welding
-
Robot painting
-
Robotics inspection
-
Robots that create products
Manufacturing could also benefit from automation in other ways. For example, 3D printing allows us to make custom products without having to wait for weeks or months to get them manufactured.
What are the 7 R's of logistics?
The acronym 7Rs of Logistics refers to the seven core principles of logistics management. It was developed and published by the International Association of Business Logisticians in 2004 as part of the "Seven Principles of Logistics Management".
The acronym consists of the following letters:
-
Responsible - to ensure that all actions are within the legal requirements and are not detrimental to others.
-
Reliable - Have confidence in your ability to fulfill all of your commitments.
-
Reasonable - make sure you use your resources well and don't waste them.
-
Realistic - consider all aspects of operations, including cost-effectiveness and environmental impact.
-
Respectful - Treat people fairly and equitably
-
Resourceful - look for opportunities to save money and increase productivity.
-
Recognizable: Provide customers with value-added service
What is the responsibility of a logistics manager?
Logistics managers make sure all goods are delivered on schedule and without damage. This is done by using his/her experience and knowledge of the company's products. He/she should make sure that enough stock is on hand to meet the demands.
What is the importance of automation in manufacturing?
Automation is essential for both manufacturers and service providers. It enables them to provide services faster and more efficiently. It also helps to reduce costs and improve productivity.
How can manufacturing excess production be decreased?
Improved inventory management is the key to reducing overproduction. This would reduce time spent on activities such as purchasing, stocking, and maintaining excess stock. This would allow us to use our resources for more productive tasks.
This can be done by using a Kanban system. A Kanbanboard is a visual tool that allows you to keep track of the work being done. Kanban systems are where work items travel through a series of states until reaching their final destination. Each state represents a different priority.
If work is moving from one stage to the other, then the current task can be completed and moved on to the next. It is possible to keep a task in the beginning stages until it gets to the end.
This allows work to move forward and ensures that no work is missed. Managers can monitor the work being done by Kanban boards to see what is happening at any given time. This data allows them adjust their workflow based upon real-time data.
Lean manufacturing, another method to control inventory levels, is also an option. Lean manufacturing is about eliminating waste from all stages of the production process. Anything that doesn't add value to the product is considered waste. Here are some examples of common types.
-
Overproduction
-
Inventory
-
Unnecessary packaging
-
Materials in excess
By implementing these ideas, manufacturers can improve efficiency and cut costs.
Statistics
- Many factories witnessed a 30% increase in output due to the shift to electric motors. (en.wikipedia.org)
- Job #1 is delivering the ordered product according to specifications: color, size, brand, and quantity. (netsuite.com)
- You can multiply the result by 100 to get the total percent of monthly overhead. (investopedia.com)
- It's estimated that 10.8% of the U.S. GDP in 2020 was contributed to manufacturing. (investopedia.com)
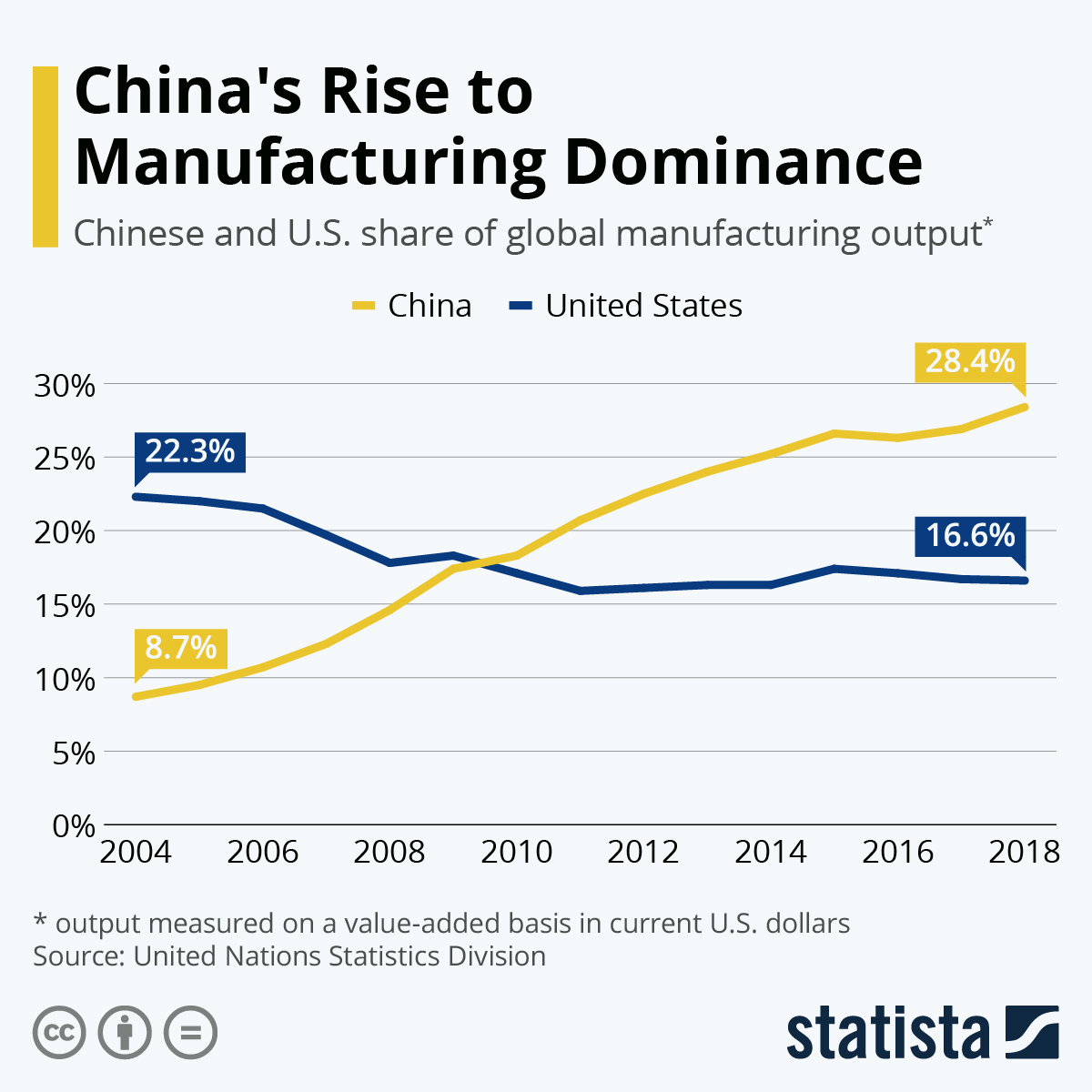
- According to the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO), China is the top manufacturer worldwide by 2019 output, producing 28.7% of the total global manufacturing output, followed by the United States, Japan, Germany, and India.[52][53] (en.wikipedia.org)
External Links
How To
How to use the Just In-Time Production Method
Just-in time (JIT), is a process that reduces costs and increases efficiency in business operations. It's a way to ensure that you get the right resources at just the right time. This means that your only pay for the resources you actually use. Frederick Taylor developed the concept while working as foreman in early 1900s. He observed how workers were paid overtime if there were delays in their work. He concluded that if workers were given enough time before they start work, productivity would increase.
JIT is a way to plan ahead and make sure you don't waste any money. Also, you should look at the whole project from start-to-finish and make sure you have the resources necessary to address any issues. You will have the resources and people to solve any problems you anticipate. You won't have to pay more for unnecessary items.
There are many JIT methods.
-
Demand-driven JIT: You order the parts and materials you need for your project every other day. This will let you track the amount of material left over after you've used it. You'll also be able to estimate how long it will take to produce more.
-
Inventory-based : You can stock the materials you need in advance. This allows you predict the amount you can expect to sell.
-
Project-driven: This method allows you to set aside enough funds for your project. If you know the amount you require, you can buy the materials you need.
-
Resource-based JIT: This is the most popular form of JIT. You allocate resources based on the demand. For example, if there is a lot of work coming in, you will have more people assigned to them. If there aren't many orders, you will assign fewer people.
-
Cost-based : This is similar in concept to resource-based. But here, you aren't concerned about how many people your company has but how much each individual costs.
-
Price-based: This is a variant of cost-based. However, instead of focusing on the individual workers' costs, this looks at the total price of the company.
-
Material-based: This is very similar to cost-based but instead of looking at total costs of the company you are concerned with how many raw materials you use on an average.
-
Time-based JIT: A variation on resource-based JIT. Instead of focusing on how much each employee costs, you focus on how long it takes to complete the project.
-
Quality-based JIT is another variant of resource-based JIT. Instead of thinking about how much each employee costs or how long it takes to manufacture something, you think about how good the quality of your product is.
-
Value-based JIT is the newest form of JIT. In this case, you're not concerned with how well the products perform or whether they meet customer expectations. Instead, you're focused on how much value you add to the market.
-
Stock-based is an inventory-based system that measures the number of items produced at any given moment. It's used when you want to maximize production while minimizing inventory.
-
Just-in-time (JIT) planning: This is a combination of JIT and supply chain management. It refers to the process of scheduling the delivery of components as soon as they are ordered. It's important as it reduces leadtimes and increases throughput.