The career of biomedical engineer can have a positive effect on people's health. This group includes engineers who work in pharmaceutical manufacturing, hospitals, and laboratories. These engineers invent new techniques and products that aid patients.
To become a biomedical engineering, you will need a bachelor's degree. Biomedical engineers should also have solid math and science foundations. They should also be able to problem solve and have strong analytical skills. Internships are another option. Employers may require a master's degree.
Biomedical engineers are expected to be in high demand due to the aging population as well as advances in medical technology. Biomedical engineering works with professionals in the medical field to test and develop new technologies. Biomedical engineers also design, manufacture, and repair medical equipment. They can work in hospitals, research facilities or medical equipment sales businesses.

Biomedical engineering uses advanced science and math in order to design equipment, software and other solutions to biological sciences problems. To create complex medical devices and models, they also use advanced math and statistics. In addition to designing new devices and processes, biomedical engineers are also responsible for testing new medications and drug therapies. Medical equipment must perform at its best.
As with any engineering field, there is a high demand for biomedical engineers. The field is expected expand faster than other engineering disciplines. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, biomedical engineering jobs will increase six percent between 2020- 2030. This is much faster that the average growth rate across all occupations. Biomedical engineers had approximately 15,700 jobs as of 2010. The BLS projects that there will 1,400 open positions each year until 2029. These openings are expected in the following industries.
Internships are an opportunity to explore a career in biomedical engineering. These internships give you the chance to learn from real-world biomedical engineers and get hands-on experience. If you are a student, it's a good idea also to take courses such as computer programming, mechanical drawing, and drafting. Individuals who love science can opt to study biology, human anatomy, and molecular biology.
If you are interested in a career as a biomedical engineering professional, it is advisable to start your preparations as early as high school. A bachelor's degree is necessary in biomedical Engineering, but employers often prefer a masters degree. A master's degree in biomedical engineering can open up new opportunities and allow you to assume supervisory positions within the field.

Biomedical engineers must take courses in physics, biology, chemistry, and mathematics. Students studying biomedical engineers study human anatomy, molecular biology, physiology and pharmacology during their undergraduate studies. They also work on capstone projects that integrate their engineering skills with problems of biological science.
FAQ
How can I find out more about manufacturing?
Experience is the best way for you to learn about manufacturing. You can also read educational videos or take classes if this isn't possible.
How does manufacturing avoid bottlenecks in production?
The key to avoiding bottlenecks in production is to keep all processes running smoothly throughout the entire production cycle, from the time you receive an order until the time when the product ships.
This includes planning for capacity requirements as well as quality control measures.
The best way to do this is to use continuous improvement techniques such as Six Sigma.
Six Sigma management is a system that improves quality and reduces waste within your organization.
It emphasizes consistency and eliminating variance in your work.
What are the 7 R's of logistics?
The 7R's of Logistics is an acronym for the seven basic principles of logistics management. It was published in 2004 by the International Association of Business Logisticians as part of their "Seven Principles of Logistics Management" series.
The following letters make up the acronym:
-
Responsible - ensure that actions are in compliance with legal requirements and do not cause harm to others.
-
Reliable: Have faith in your ability or the ability to honor any promises made.
-
It is reasonable to use resources efficiently and not waste them.
-
Realistic – consider all aspects of operations, from cost-effectiveness to environmental impact.
-
Respectful – Treat others fairly and equitably.
-
Be resourceful: Look for opportunities to save money or increase productivity.
-
Recognizable - provide customers with value-added services.
What are manufacturing & logistics?
Manufacturing refers the process of producing goods from raw materials through machines and processes. Logistics covers all aspects involved in managing supply chains, including procurement and production planning. Manufacturing and logistics are often considered together as a broader term that encompasses both the process of creating products and delivering them to customers.
Statistics
- (2:04) MTO is a production technique wherein products are customized according to customer specifications, and production only starts after an order is received. (oracle.com)
- In the United States, for example, manufacturing makes up 15% of the economic output. (twi-global.com)
- In 2021, an estimated 12.1 million Americans work in the manufacturing sector.6 (investopedia.com)
- According to a Statista study, U.S. businesses spent $1.63 trillion on logistics in 2019, moving goods from origin to end user through various supply chain network segments. (netsuite.com)
- It's estimated that 10.8% of the U.S. GDP in 2020 was contributed to manufacturing. (investopedia.com)
External Links
How To
How to Use lean manufacturing in the Production of Goods
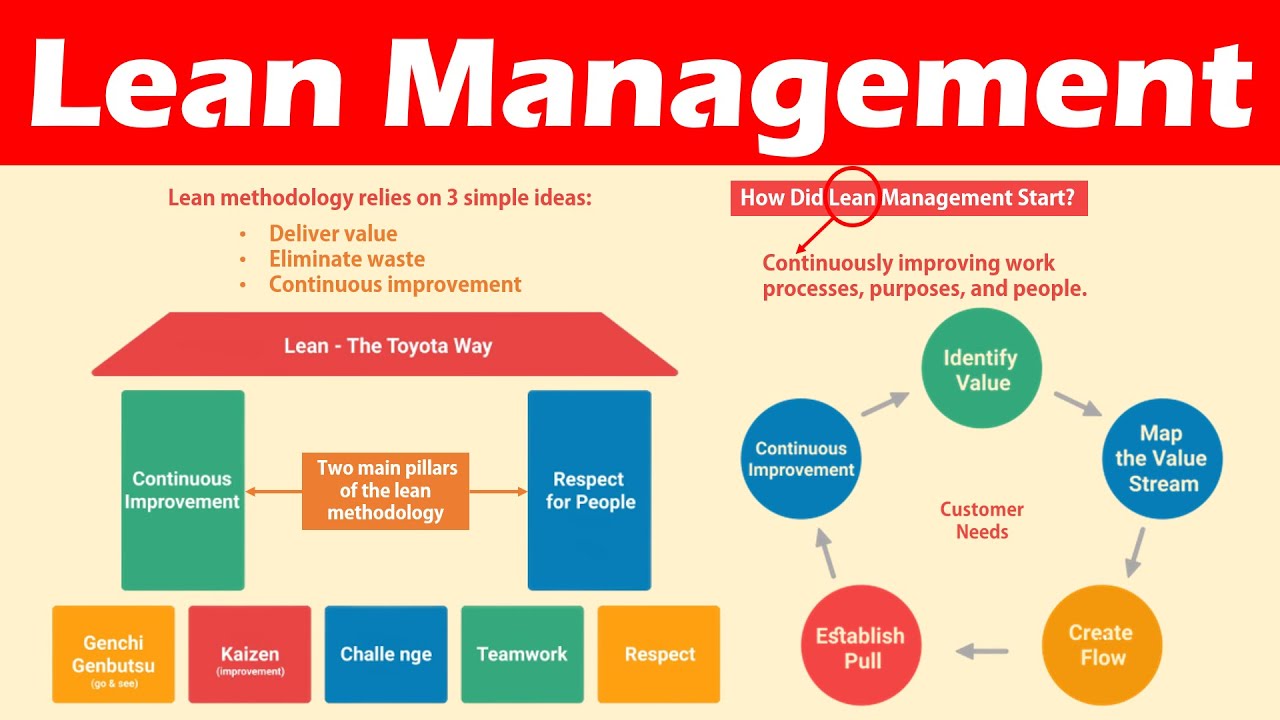
Lean manufacturing (or lean manufacturing) is a style of management that aims to increase efficiency, reduce waste and improve performance through continuous improvement. It was created in Japan by Taiichi Ohno during the 1970s and 80s. He received the Toyota Production System award (TPS), from Kanji Toyoda, founder of TPS. Michael L. Watkins published the "The Machine That Changed the World", the first book about lean manufacturing. It was published in 1990.
Lean manufacturing is often described as a set if principles that help improve the quality and speed of products and services. It emphasizes the elimination and minimization of waste in the value stream. Just-in-time (JIT), zero defect (TPM), and 5S are all examples of lean manufacturing. Lean manufacturing is about eliminating activities that do not add value, such as inspection, rework, and waiting.
Lean manufacturing not only improves product quality but also reduces costs. Companies can also achieve their goals faster by reducing employee turnover. Lean manufacturing is considered one of the most effective ways to manage the entire value chain, including suppliers, customers, distributors, retailers, and employees. Lean manufacturing is widely practiced in many industries around the world. Toyota's philosophy is a great example of this. It has helped to create success in automobiles as well electronics, appliances and healthcare.
Five fundamental principles underlie lean manufacturing.
-
Define Value: Identify the social value of your business and what sets you apart.
-
Reduce Waste – Eliminate all activities that don't add value throughout the supply chain.
-
Create Flow. Ensure that your work is uninterrupted and flows seamlessly.
-
Standardize and simplify – Make processes as repeatable and consistent as possible.
-
Build relationships - Develop and maintain personal relationships with both your internal and external stakeholders.
Lean manufacturing, although not new, has seen renewed interest in the economic sector since 2008. To increase their competitiveness, many businesses have turned to lean manufacturing. Many economists believe lean manufacturing will play a major role in economic recovery.
Lean manufacturing is becoming a popular practice in automotive. It has many advantages. These include higher customer satisfaction levels, reduced inventory levels as well as lower operating costs.
Any aspect of an enterprise can benefit from Lean manufacturing. This is because it ensures efficiency and effectiveness in all stages of the value chain.
There are three types principally of lean manufacturing:
-
Just-in Time Manufacturing, (JIT): This kind of lean manufacturing is also commonly known as "pull-systems." JIT means that components are assembled at the time of use and not manufactured in advance. This method reduces lead times, increases availability, and decreases inventory.
-
Zero Defects Manufacturing - ZDM: ZDM focuses its efforts on making sure that no defective units leave a manufacturing facility. You should repair any part that needs to be repaired during an assembly line. This also applies to finished products that need minor repairs before being shipped.
-
Continuous Improvement (CI: Continuous improvement aims to increase the efficiency of operations by constantly identifying and making improvements to reduce or eliminate waste. Continuous Improvement (CI) involves continuous improvement in processes, people, tools, and infrastructure.