
The location you work and the area you specialize will determine how much you can make as a material engineer. Apple, ConocoPhillips Meta, Western Digital and Meta are the most well-paid. Others, such as FedEx and Motorola Solutions, can also be excellent places for a material engineer to work.
Materials engineers need to understand the relationship between materials and their processing methods. They must also be capable of identifying the causes and consequences of failures. Aside from being able to explain engineering concepts and ideas to non-engineers, they also need to be able to do so. They are responsible for developing and implementing cost-efficient operations strategies. They might also be required to communicate with suppliers or other professionals. They might also need to travel to different countries to collect samples. In some cases they may have to work for more than 40 hours per week.
Advanced degrees may be available for materials engineers. They might be eligible to do a PhD in process engineer. They may also be able find research positions or teaching jobs. Senior material engineers might have more managerial responsibilities. They might also have the opportunity for innovative research.

Materials engineers might work in offices and manufacturing plants, but they may also travel to the workplace to collect samples. The field is very competitive and it is important that you stay up to date with industry innovations and trends. Aside from that, they might need to build relationships with clients. They can provide green practices to product engineers and help them improve their products. They may also be able build a strong reputation within their field.
Materials engineers might also work at laboratories. They may also use advanced math topics in design and troubleshooting. They may need to communicate engineering concepts clearly. They may be required to travel overseas to collect samples or to observe manufacturing processes in other countries.
Materials engineers are typically hired by technology companies, such as Apple and FedEx. Raytheon Technologies is one example of a company that employs materials engineers. This industry is highly competitive so it might be difficult for you to find a job at these companies. Through engineering consulting firms, it is possible to be a materialist. You may also have the opportunity to start your own business, which will allow you to stay at the forefront of your industry.
Long hours may be required for materials engineers. They may be required to travel to sites in order to test materials or observe the manufacturing process. If they are working in a factory, they may be expected to work 40-hour days. This means they might need to have a strong work ethic.
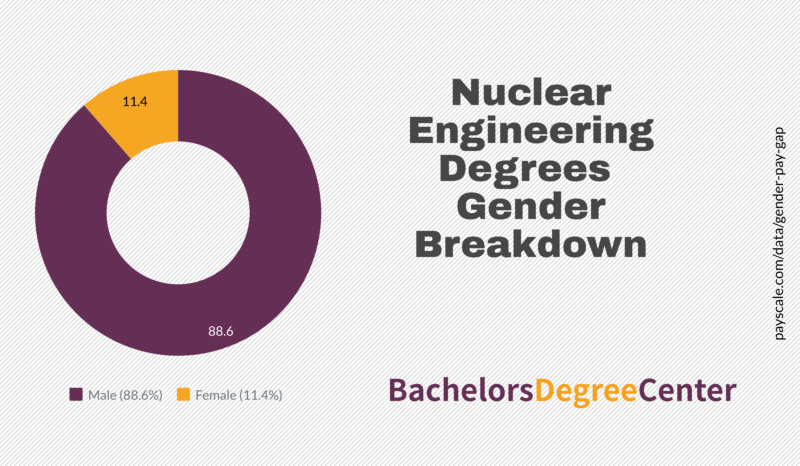
As a result, material engineers may need to work with a team. They may also need to communicate regularly with clients and suppliers. They may also be responsible for meeting deadlines and budgets.
FAQ
What is meant by manufacturing industries?
Manufacturing Industries refers to businesses that manufacture products. The people who buy these products are called consumers. These companies employ many processes to achieve this purpose, such as production and distribution, retailing, management and so on. They create goods from raw materials, using machines and various other equipment. This includes all types and varieties of manufactured goods, such as food items, clothings, building supplies, furnitures, toys, electronics tools, machinery vehicles, pharmaceuticals medical devices, chemicals, among others.
What is the distinction between Production Planning or Scheduling?
Production Planning (PP) refers to the process of determining how much production is needed at any given moment. This is done through forecasting demand and identifying production capacities.
Scheduling refers to the process of allocating specific dates to tasks in order that they can be completed within a specified timeframe.
How can overproduction in manufacturing be reduced?
Improved inventory management is the key to reducing overproduction. This would decrease the time that is spent on inefficient activities like purchasing, storing, or maintaining excess stock. By doing this, we could free up resources for other productive tasks.
Kanban systems are one way to achieve this. A Kanban board, a visual display to show the progress of work, is called a Kanban board. In a Kanban system, work items move through a sequence of states until they reach their final destination. Each state is assigned a different priority.
If work is moving from one stage to the other, then the current task can be completed and moved on to the next. However, if a task is still at the beginning stages, it will remain so until it reaches the end of the process.
This helps to keep work moving forward while ensuring that no work is left behind. With a Kanban board, managers can see exactly how much work is being done at any given moment. This information allows them to adjust their workflow based on real-time data.
Lean manufacturing can also be used to reduce inventory levels. Lean manufacturing emphasizes eliminating waste in all phases of production. Anything that does nothing to add value to a product is waste. The following are examples of common waste types:
-
Overproduction
-
Inventory
-
Packaging not required
-
Excess materials
By implementing these ideas, manufacturers can improve efficiency and cut costs.
How can manufacturing avoid production bottlenecks
To avoid production bottlenecks, ensure that all processes run smoothly from the moment you receive your order to the time the product ships.
This includes planning to meet capacity requirements and quality control.
The best way to do this is to use continuous improvement techniques such as Six Sigma.
Six Sigma is a management method that helps to improve quality and reduce waste.
It's all about eliminating variation and creating consistency in work.
What are the 7 Rs of logistics?
The acronym 7Rs of Logistics refers to the seven core principles of logistics management. It was developed by International Association of Business Logisticians (IABL), and published as part of their "Seven Principles of Logistics Management Series" in 2004.
The acronym is composed of the following letters.
-
Responsible - ensure that all actions taken are within legal requirements and are not harmful to others.
-
Reliable - Have confidence in your ability to fulfill all of your commitments.
-
Reasonable - use resources efficiently and don't waste them.
-
Realistic - consider all aspects of operations, including cost-effectiveness and environmental impact.
-
Respectful: Treat others with fairness and equity
-
You are resourceful and look for ways to save money while increasing productivity.
-
Recognizable is a company that provides customers with value-added solutions.
How can efficiency in manufacturing be improved?
The first step is to determine the key factors that impact production time. Then we need to find ways to improve these factors. If you don't know where to start, then think about which factor(s) have the biggest impact on production time. Once you have identified them, it is time to identify solutions.
What jobs are available in logistics?
Logistics can offer many different jobs. Some examples are:
-
Warehouse workers – They load, unload and transport pallets and trucks.
-
Transportation drivers – They drive trucks or trailers to transport goods and perform pick-ups.
-
Freight handlers are people who sort and pack freight into warehouses.
-
Inventory managers: They are responsible for the inventory and management of warehouses.
-
Sales representatives - They sell products to customers.
-
Logistics coordinators - They plan and organize logistics operations.
-
Purchasing agents – They buy goods or services necessary to run a company.
-
Customer service representatives - They answer calls and emails from customers.
-
Shipping clerks - They process shipping orders and issue bills.
-
Order fillers – They fill orders based upon what was ordered and shipped.
-
Quality control inspectors – They inspect incoming and outgoing products to ensure that there are no defects.
-
Others - There is a variety of other jobs in logistics. These include transportation supervisors and cargo specialists.
Statistics
- You can multiply the result by 100 to get the total percent of monthly overhead. (investopedia.com)
- In 2021, an estimated 12.1 million Americans work in the manufacturing sector.6 (investopedia.com)
- (2:04) MTO is a production technique wherein products are customized according to customer specifications, and production only starts after an order is received. (oracle.com)
- It's estimated that 10.8% of the U.S. GDP in 2020 was contributed to manufacturing. (investopedia.com)
- According to the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO), China is the top manufacturer worldwide by 2019 output, producing 28.7% of the total global manufacturing output, followed by the United States, Japan, Germany, and India.[52][53] (en.wikipedia.org)
External Links
How To
Six Sigma in Manufacturing:
Six Sigma refers to "the application and control of statistical processes (SPC) techniques in order to achieve continuous improvement." Motorola's Quality Improvement Department created Six Sigma at their Tokyo plant, Japan in 1986. The basic idea behind Six Sigma is to improve quality by improving processes through standardization and eliminating defects. In recent years, many companies have adopted this method because they believe there is no such thing as perfect products or services. Six Sigma's primary goal is to reduce variation from the average value of production. This means that you can take a sample from your product and then compare its performance to the average to find out how often the process differs from the norm. If you notice a large deviation, then it is time to fix it.
Understanding how variability works in your company is the first step to Six Sigma. Once you have this understanding, you will need to identify sources and causes of variation. This will allow you to decide if these variations are random and systematic. Random variations are caused by human errors. Systematic variations can be caused by outside factors. For example, if you're making widgets, and some of them fall off the assembly line, those would be considered random variations. You might notice that your widgets always fall apart at the same place every time you put them together.
Once you've identified where the problems lie, you'll want to design solutions to eliminate those problems. It might mean changing the way you do business or redesigning it entirely. Test them again once you've implemented the changes. If they don’t work, you’ll need to go back and rework the plan.