
For successful operation of Anthropomorphic or Articulated-arm robotic arms, it is crucial to have an understanding of the basics. This article will describe the differences and explain how the Sensor and Mechanical units work together in an arm robot. To further understand the differences, we will examine what each one is capable of, and how it can help our daily lives. These are important design considerations. It is important to consider the weight and size of the component that will be handled as well as the required gripper. Also, the attachment's weight must be equal to or less than the component to be grasped. A particular attachment may have a far-away centre of gravity that would require a heavier payload.
Articulated-arm robotics
Amazing versatility is possible with Articulated-arm robotics. Each six-axis unit has a flexible arm similar to a human arm. It moves around its base and bends at the middle, much like a human's elbow. ArticulatedArm robots' wrists can also move in an arched fashion, similar to a human's. The robot can also rotate its fingers. This allows the robot grasp any object at any place on the component.
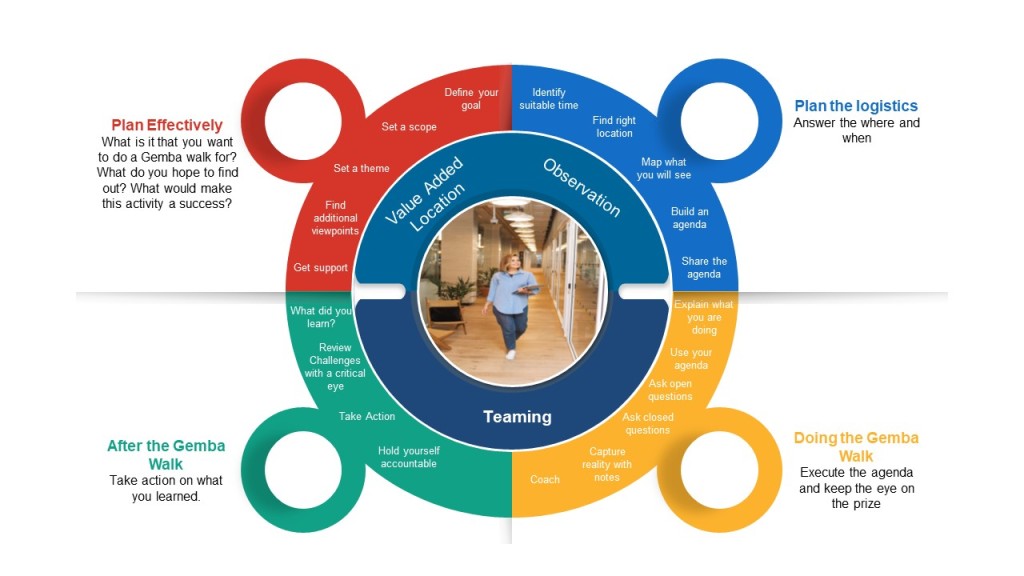
Anthropomorphic robotic arms
Anthropomorphic Robot Arms are robots that can imitate human arm movement. These robotic arms can handle different objects such as items of different sizes. Tele-replication is used to replicate human motion and implement operator's movements. These robots were tested and proved useful in numerous applications. Researchers developed a method to interpret the movements of the human operator, and then implement them into the robot arm.
Arm robots with mechanical units
The mechanical unit of arm robots has many functions. The robotic wrist allows the end effector (the tool that holds an item) to be placed on a piece of work-piece. Two rotary joints are located on the wrist. One allows the end-effector rotates and the other allows it to move in a specific direction. The wrist and the end-effector both have different degrees of freedom. These units can also be used together to transport parts on pallets.
Sensor unit in arm robots
An arm robotics system includes a sensor unit that detects and recognizes changes in body temperature. This sensor is placed on the robotic arm's gripper end, where it can contact a temperature-measurement object. It sends a signal back to the STM32 microcomputer embedded in the base of the robotic arm when it detects temperature changes. The STM32 controls the actions of the robot, and when it senses that the temperature has reached dangerous levels, the STM32 sends an alert to the operator. During normal operations, it won't be necessary to interrupt the robot.
Cost to join an arm robot
If you're looking to build a robotic arm, you may wonder how much it costs. There are many factors that affect the cost of an arm robotic arm. These include the size and number of axes used, safety components and end-of-arm tooling. As well as the cost of additional peripherals and tools, the larger the robot will be the more expensive it will cost. Apart from the robot's size, an additional factor that affects cost is its application. The payload of a larger robot is greater and it can reach greater distances. However, the additional cost of safety features is often offset by its greater size.
FAQ
What are the responsibilities of a logistic manager?
Logistics managers are responsible for ensuring that all goods arrive in perfect condition and on time. This is achieved by using their knowledge and experience with the products of the company. He/she must also ensure sufficient stock to meet the demand.
What do you mean by warehouse?
A warehouse, or storage facility, is where goods are stored prior to being sold. It can be an outdoor or indoor area. Sometimes, it can be both an indoor and outdoor space.
What is the best way to learn about manufacturing?
Experience is the best way for you to learn about manufacturing. But if that is not possible you can always read books and watch educational videos.
Statistics
- According to a Statista study, U.S. businesses spent $1.63 trillion on logistics in 2019, moving goods from origin to end user through various supply chain network segments. (netsuite.com)
- (2:04) MTO is a production technique wherein products are customized according to customer specifications, and production only starts after an order is received. (oracle.com)
- It's estimated that 10.8% of the U.S. GDP in 2020 was contributed to manufacturing. (investopedia.com)
- Job #1 is delivering the ordered product according to specifications: color, size, brand, and quantity. (netsuite.com)
- [54][55] These are the top 50 countries by the total value of manufacturing output in US dollars for its noted year according to World Bank.[56] (en.wikipedia.org)
External Links
How To
How to use Lean Manufacturing in the production of goods
Lean manufacturing (or lean manufacturing) is a style of management that aims to increase efficiency, reduce waste and improve performance through continuous improvement. It was developed in Japan between 1970 and 1980 by Taiichi Ohno. TPS founder Kanji Tyoda gave him the Toyota Production System, or TPS award. Michael L. Watkins published the book "The Machine That Changed the World", which was the first to be published about lean manufacturing.
Lean manufacturing refers to a set of principles that improve the quality, speed and costs of products and services. It emphasizes eliminating waste and defects throughout the value stream. The five-steps of Lean Manufacturing are just-in time (JIT), zero defect and total productive maintenance (TPM), as well as 5S. Lean manufacturing focuses on eliminating non-value-added activities such as rework, inspection, and waiting.
Lean manufacturing is a way for companies to achieve their goals faster, improve product quality, and lower costs. Lean manufacturing is a great way to manage the entire value chain including customers, suppliers, distributors and retailers as well as employees. Lean manufacturing practices are widespread in many industries. Toyota's philosophy is the foundation of its success in automotives, electronics and appliances, healthcare, chemical engineers, aerospace, paper and food, among other industries.
Lean manufacturing is based on five principles:
-
Define value - Find out what your business contributes to society, and what makes it different from other competitors.
-
Reduce Waste - Remove any activity which doesn't add value to your supply chain.
-
Create Flow: Ensure that the work process flows without interruptions.
-
Standardize & simplify - Make processes consistent and repeatable.
-
Building Relationships – Establish personal relationships with both external and internal stakeholders.
Although lean manufacturing isn't a new concept in business, it has gained popularity due to renewed interest in the economy after the 2008 global financial crisis. Many companies have adopted lean manufacturing methods to increase their marketability. Many economists believe lean manufacturing will play a major role in economic recovery.
With many benefits, lean manufacturing is becoming more common in the automotive industry. These benefits include increased customer satisfaction, reduced inventory levels and lower operating costs.
You can apply Lean Manufacturing to virtually any aspect of your organization. It is especially useful for the production aspect of an organization, as it ensures that every step in the value chain is efficient and effective.
There are three main types of lean manufacturing:
-
Just-in-Time Manufacturing (JIT): This type of lean manufacturing is commonly referred to as "pull systems." JIT is a method in which components are assembled right at the moment of use, rather than being manufactured ahead of time. This approach is designed to reduce lead times and increase the availability of components. It also reduces inventory.
-
Zero Defects Manufacturing (ZDM),: ZDM is a system that ensures no defective units are left the manufacturing facility. It is better to repair a part than have it removed from the production line if it needs to be fixed. This is true even for finished products that only require minor repairs prior to shipping.
-
Continuous Improvement (CI): CI aims to improve the efficiency of operations by continuously identifying problems and making changes in order to eliminate or minimize waste. Continuous Improvement involves continuous improvement of processes.